Single-Agent Pattern
A single agent is an autonomous AI system that can reason, plan, and execute actions through iterative tool calling within a single workflow execution. The agent loops internally until it completes the task, reaches iteration limits, or hits a Stop Node.Architecture
A single agent is built using a Subflow Node containing:- Start Node - Entry point for each iteration
- LLM Node - The “brain” that reasons, decides actions, and calls tools autonomously
- Tool Nodes - Connected to LLM via TOOLS handle (automatic tool discovery and calling)
- Memory Node - Connected to LLM via MEMORY handle (maintains conversation history across iterations)
- End Node - Marks the end of one iteration (loop continues if iterations remain)
- Stop Node (optional) - Force-terminates the entire subflow immediately when reached
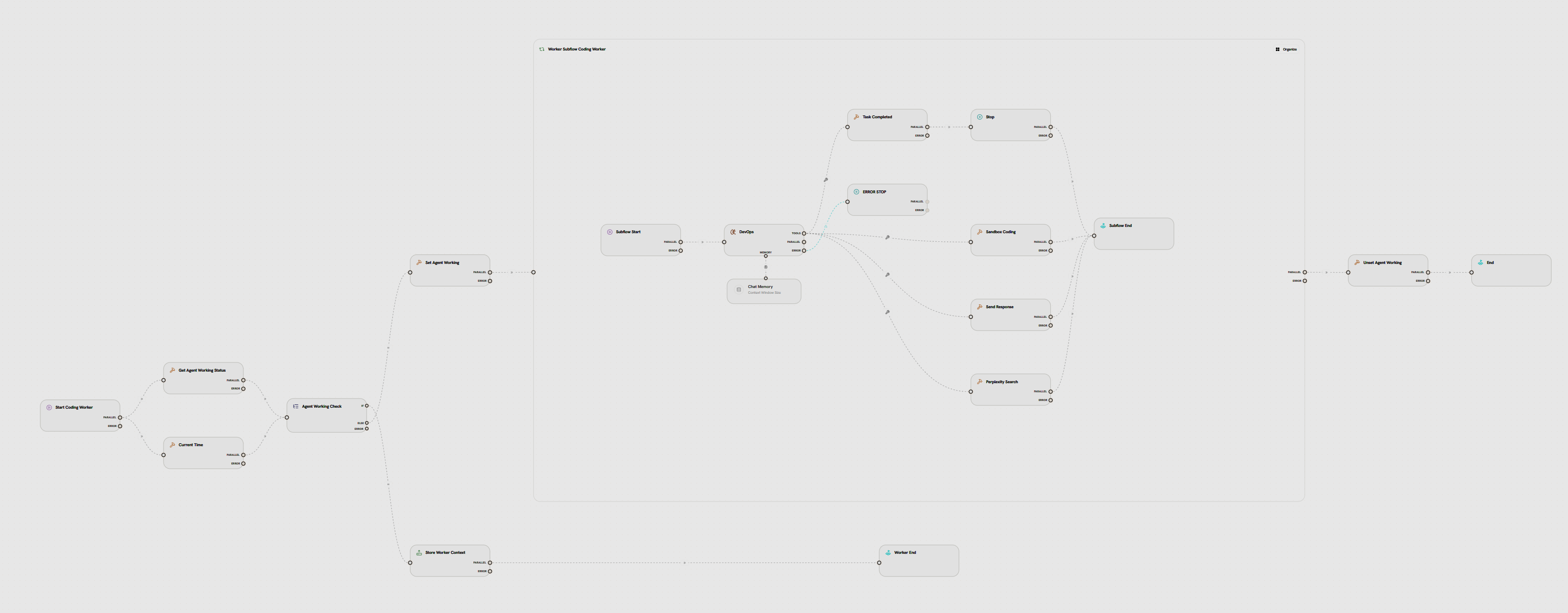
- Agent Loop (Subflow)
- LLM + Tools
- Memory Connection
- Loop Control
The entire pattern is enclosed in a Subflow Node configured for agent operation:Configuration:
- Iterate Over: Number of Times (Count)
- Number of Iterations: 10-50 (depending on task complexity)
- Execution Mode: Sequential (one iteration at a time)
- Stop Node is reached (immediate force-exit)
- Number of Iterations limit is hit
- Timeout occurs
The subflow structure enables proactive multi-turn tool calling - the LLM can autonomously call multiple tools within a single workflow execution without external triggers.
Iteration Flow
End Node vs Stop Node
- End Node: Completes one iteration. If Number of Iterations not reached, the loop continues from Start Node via LOOP handle
- Stop Node: Immediately terminates the entire subflow with ForceFinish flag, regardless of remaining iterations
- Place after tools that indicate task completion (e.g., “send_final_response”, “task_complete”)
- Prevent unnecessary iterations when agent knows it’s done
- Exit early on error conditions or resource limits
How It Works
1
Iteration Starts
User input enters the subflow via the Start NodeExample: “Book a meeting with John for tomorrow at 2pm”Each iteration begins fresh from the Start Node. The subflow is configured with:
- Iterate Over: Number of Times (Count)
- Number of Iterations: e.g., 10
- Execution Mode: Sequential
2
LLM Analyzes and Decides
The LLM node receives:
- Current user input (or previous tool results from last iteration)
- Conversation history (from MEMORY handle)
- Available tools (automatically discovered from TOOLS handle connections)
3
Tool Execution (Proactive)
If the LLM calls a tool:
- Generates structured tool call with parameters
- Tool executes automatically
- Results return immediately to LLM (within same execution)
- Flow continues to End Node or Stop Node
check_calendar tool with date=“tomorrow”Key Difference: Unlike reactive tool calling (main workflow), results don’t wait for external trigger - they’re immediately available to the LLM in the next iteration4
Iteration Completes
The iteration reaches End Node or Stop NodeIf End Node reached:
- Iteration completes
- If Number of Iterations not reached → LOOP handle triggers new iteration (back to Start)
- If limit reached → Subflow exits
- ForceFinish flag set
- Subflow terminates immediately
- Remaining iterations bypassed
5
Loop Repeats (Autonomous)
Each iteration can (within same execution):
- Call different tools based on previous results
- Build on conversation history in memory
- Make complex multi-step decisions autonomously
- Iteration 1: LLM checks calendar → finds conflict → calls End Node
- Iteration 2: LLM sees conflict in memory → suggests alternative → calls End Node
- Iteration 3: LLM confirms with user → sends invite → calls Stop Node → Done
6
Final Exit
Subflow exits when:
- Stop Node is reached (force finish)
- Number of Iterations limit hit
- Timeout occurs
Creating a Single Agent
1
Add Subflow Node
Drag a Subflow Node onto the canvas from the node menu
2
Configure Subflow for Agent Pattern
Set the subflow node configuration:
- Label: “Customer Support Agent”
- Iterate Over: Number of Times (Count)
- Number of Iterations: 10 (adjust based on task complexity)
- Execution Mode: Sequential (one iteration at a time)
- Delay Between Iterations: 0 seconds (no delay for agents)
3
Enter Subflow Context
Double-click the subflow node to enter its internal workflowThe canvas zooms into the subflow’s contained nodes
4
Build Agent Logic
Inside the subflow:
- Start Node (auto-created)
- Add LLM Node with system prompt defining agent behavior
- Add Tool Nodes and connect to LLM via TOOLS handle
- Add Memory Node and connect to LLM via MEMORY handle
- Configure Chat ID:
agent-{{ start.user_id }}(for multi-user) - Choose Memory Limit Type: Messages or Tokens
- Set Trim Strategy and optional Summarization
- Configure Chat ID:
- Add End Node (connect regular tools here - allows loop)
- Add Stop Node (optional - connect completion tools here)
- Tools that gather info → End Node (loop continues)
- Final action tool (e.g., “send_response”) → Stop Node (force exit)
5
Exit Subflow
Click the “Exit Subflow” button or breadcrumb to return to main workflow
Configuration
Number of Iterations
Number of Iterations
Maximum number of times the subflow can execute
- Prevents infinite loops
- Field name: “Number of Iterations” (in Subflow Node config)
- Minimum: 1
- Recommended: 10-20 for agent patterns
- Customer support agent: 5-10 iterations (search, query, respond)
- Research agent: 20-50 iterations (multiple searches, cross-referencing)
- Code assistant: 10-30 iterations (read, generate, test, fix)
Delay Between Iterations
Delay Between Iterations
Wait time between iterations (in seconds)
- Default: 0 (no delay)
- For agents, always use 0 (immediate autonomous operation)
- Only use delays for rate-limiting external APIs
Execution Mode
Execution Mode
How iterations execute
- Sequential: One iteration at a time (required for agents)
- Parallel: All iterations run concurrently (for batch processing only)
Memory Configuration
Memory Configuration
Chat Memory settings for agent contextEssential Fields:
- Chat ID:
agent-{{ start.user_id }}(isolate by user) - Memory Limit Type:
- By Message Count (simple, predictable)
- By Token Count (precise control for long conversations industrialization)
- Trim Strategy:
- Drop Oldest (keep recent context)
- Drop Middle (preserve initial + recent)
- Enable Summarization: Optional (condense old messages to save tokens)
Timeout
Timeout
Maximum total execution time
- Prevents runaway execution
- Applies to entire subflow (all iterations combined)
- Default: 300 seconds (5 minutes)
Use Cases
Customer Support
Autonomous support agent
- Search knowledge base
- Check account status
- Create tickets
- Send responses
Research Assistant
Multi-step research
- Search multiple sources
- Summarize findings
- Cross-reference facts
- Compile reports
Code Assistant
Automated development
- Read code files
- Generate solutions
- Run tests
- Fix errors
Data Analysis
Autonomous analytics
- Query databases
- Generate visualizations
- Run calculations
- Create reports
Best Practices
Set Reasonable Max Iterations
Set Reasonable Max Iterations
Don’t let agents loop forever
- Simple tasks: 5-10 iterations
- Complex reasoning: 20-50 iterations
- Research/analysis: 30-100 iterations
Use Stop Node for Completion
Use Stop Node for Completion
Terminate immediately when doneAdd Stop Node after tools that indicate task completion:
send_final_responsecreate_reportfinish_task
Clear Tool Descriptions
Clear Tool Descriptions
Help LLM choose the right tool
- Explain when to use each tool
- Provide example scenarios
- Specify required parameters
- Document return values
Use Memory for Context
Use Memory for Context
Maintain conversation stateConnect Memory Node to LLM via memory edge:
- Agent remembers previous interactions
- Builds on past tool results
- Enables multi-turn conversations
- Provides coherent responses
Monitor and Optimize
Monitor and Optimize
Track agent performance
- Iteration count (are you hitting max?)
- Tool call patterns (unused tools?)
- Memory usage (token limits?)
- Cost per execution
Common Issues
Agent Loops Unnecessarily
Agent Loops Unnecessarily
Symptom: Agent hits max_iterations repeatedlySolutions:
- Make system prompt clearer about when to stop
- Add explicit completion criteria
- Improve tool descriptions
- Reduce max_iterations to force efficiency
- Add Stop Node after completion tools
Wrong Tool Selection
Wrong Tool Selection
Symptom: LLM calls inappropriate toolsSolutions:
- Improve tool descriptions with use cases
- Add examples to system prompt
- Reduce number of available tools
- Use tool categories/namespaces
Memory Overflow
Memory Overflow
Symptom: Token limits exceededSolutions:
- Enable memory summarization
- Reduce context window size
- Clear memory periodically
- Use selective memory loading
High Costs
High Costs
Symptom: Expensive LLM API billsSolutions:
- Reduce max_iterations
- Use smaller/cheaper models
- Cache repeated queries
- Optimize system prompts
- Add Stop Node to prevent extra iterations

