Error Edges
Purpose: Handle errors and failures in workflow execution Error edges create alternative paths for when nodes fail, enabling graceful error handling and recovery.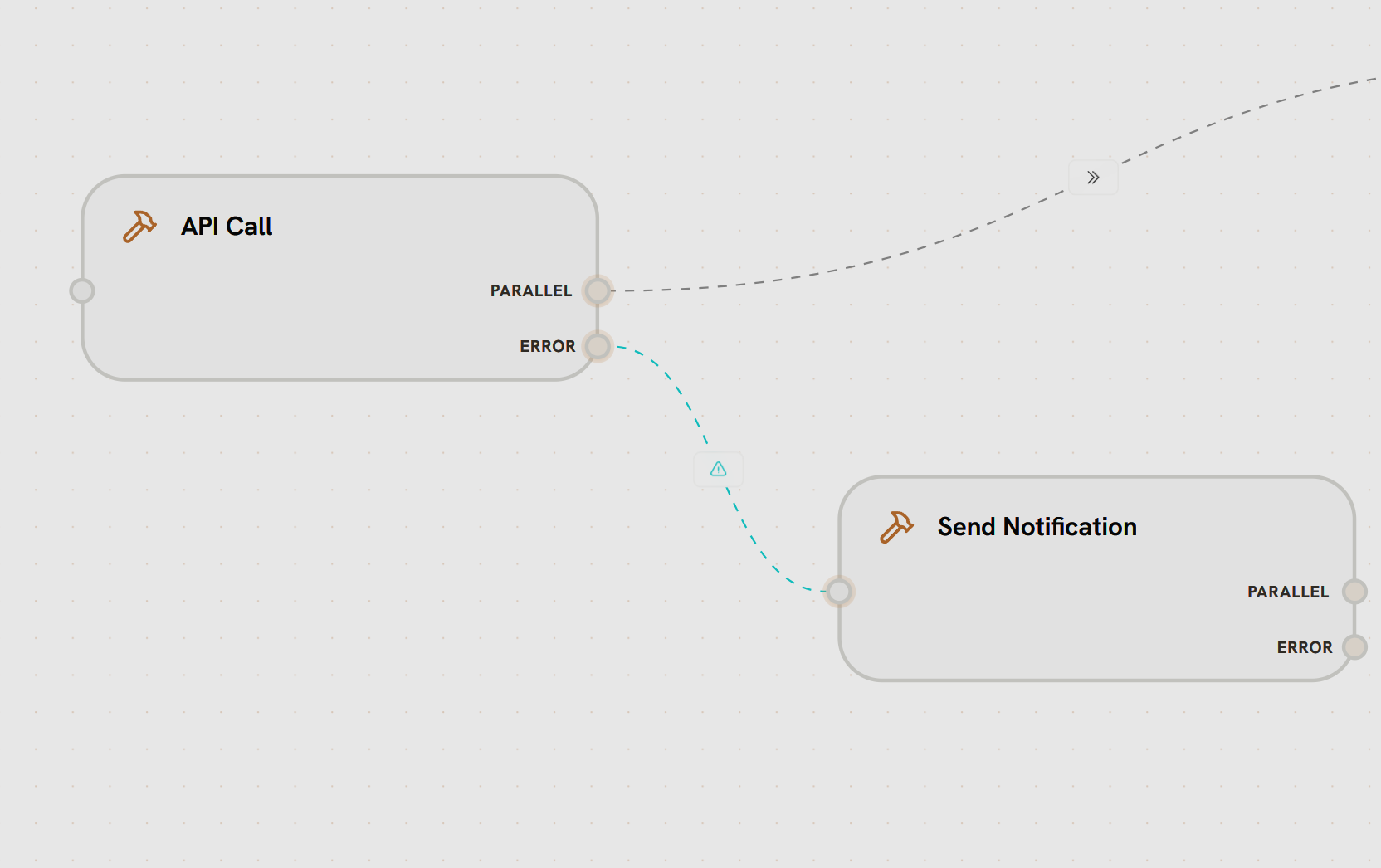
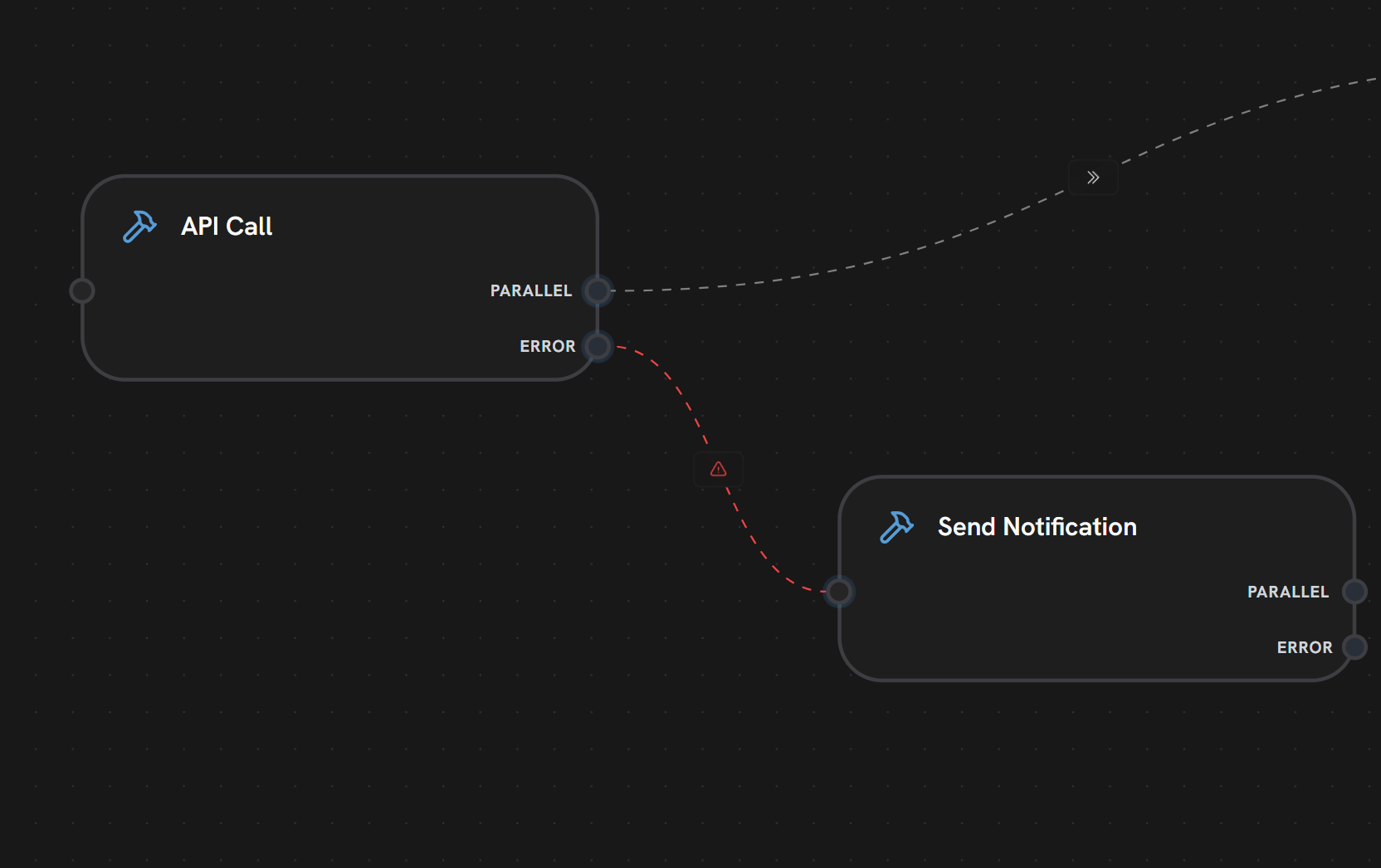
- API Call node has both PARALLEL and ERROR output handles
- PARALLEL edge (gray dashed) routes to success path (shown partially)
- ERROR edge (red dashed line with warning icon) connects to Send Notification
- If API Call fails, execution follows the red error edge
- Send Notification handles the failure (alerting, logging, recovery)
- Visual Style: Red dashed line with warning icon ⚠️
- Failure Routing: Activates only when source node fails
- Separate Path: Distinct from normal execution flow
- Error Data: Passes error information to handler node
Use Cases:
- API failure handling
- Retry logic
- Alerting and notifications
- Graceful degradation
- Error logging

