Overview
Flow control nodes manage how workflows branch, merge, iterate, and nest.Switch Node
Conditional branching based on data evaluation
Merge Node
Combine multiple execution paths
Subflow Node
Create reusable nested workflows
Switch Node
Purpose: Conditional branching based on data evaluation Switch nodes evaluate conditions and route execution to different paths.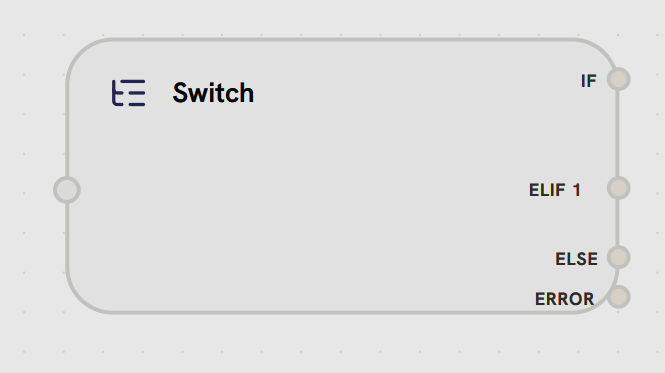
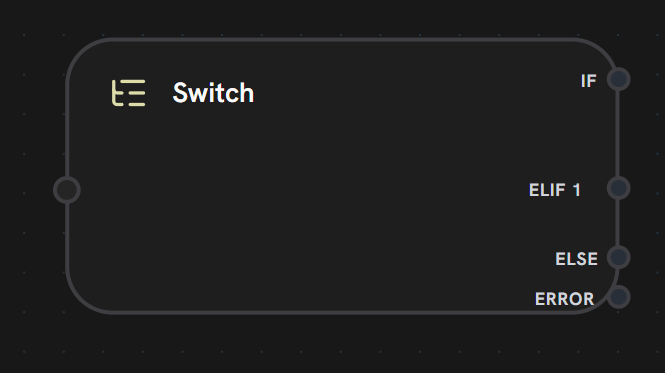
- Input Handle
- Output Handles
Left Side - Condition InputReceives data to evaluate against conditional branches.Accepts:
- Workflow variables
- Previous node outputs
- Template expressions
- Any data for conditional evaluation
Switch nodes support dynamic branching: you can add multiple ELIF branches for complex conditional logic. Branches are evaluated in order: IF → ELIF 1 → ELIF 2 → … → ELSE.
String Matching (6 operators)
String Matching (6 operators)
Check if value contains substring (case-insensitive)Example:
"Hello World" contains "world" → trueCheck if value does not contain substringExample:
"Hello World" not_contains "xyz" → trueExact match comparison (case-insensitive)Example:
"admin" equals "ADMIN" → trueNot equal comparisonExample:
"user" not_equals "admin" → trueCheck if value starts with prefixExample:
"Hello World" starts_with "Hello" → trueCheck if value ends with suffixExample:
"file.pdf" ends_with ".pdf" → trueList Operations (2 operators)
List Operations (2 operators)
Empty & Boolean Checks (4 operators)
Empty & Boolean Checks (4 operators)
Check if value is empty, null,
[], or {}Example: "" is_empty → trueCheck if value has contentExample:
"Hello" is_not_empty → trueCheck if value is truthy (
true, 1, yes, y)Example: "true" is_true → trueCheck if value is falsy (
false, 0, no, n)Example: "false" is_false → trueUnary operators (
is_empty, is_not_empty, is_true, is_false) don’t require a right operand.- AND Logic
- OR Logic
All conditions must be trueUse for: Strict validation, multiple requirement checks
- IF: First condition evaluated
- ELIF: Additional conditions (evaluated if previous failed)
- ELSE: Default path if no conditions match
- Content moderation (check for inappropriate content)
- User role routing (admin vs. user paths)
- Error handling (check for error states)
- A/B testing (route based on user segment)
Merge Node
Purpose: Combine data from multiple parallel paths Merge nodes wait for all incoming connections to complete, then combine their outputs.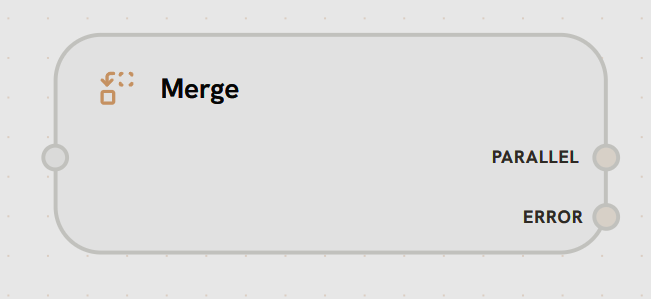
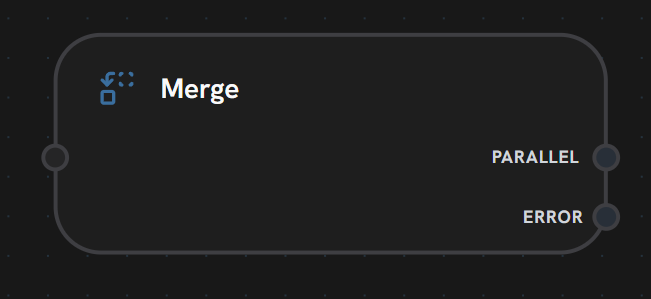
- Input Handle
- Output Handles
Left Side - Multiple InputsAccepts multiple incoming connections from parallel paths.Functionality:
- Waits for all connected inputs to complete
- Receives data from each parallel branch
- Synchronizes parallel execution
- Multiple node outputs
- Parallel branch results
- Any data to merge
Merge nodes act as synchronization points in workflows. They wait for ALL incoming connections to complete before executing the merge operation and continuing.
- Object Merge
- Array Merge
- First Complete
Combine objects into single object
- Parallel API calls with combined results
- Multi-agent responses aggregation
- Redundant path execution (use fastest)
- Batch processing collection
Subflow Node
Purpose: Execute reusable workflow components Subflow nodes contain nested workflows that can be reused across multiple parent workflows.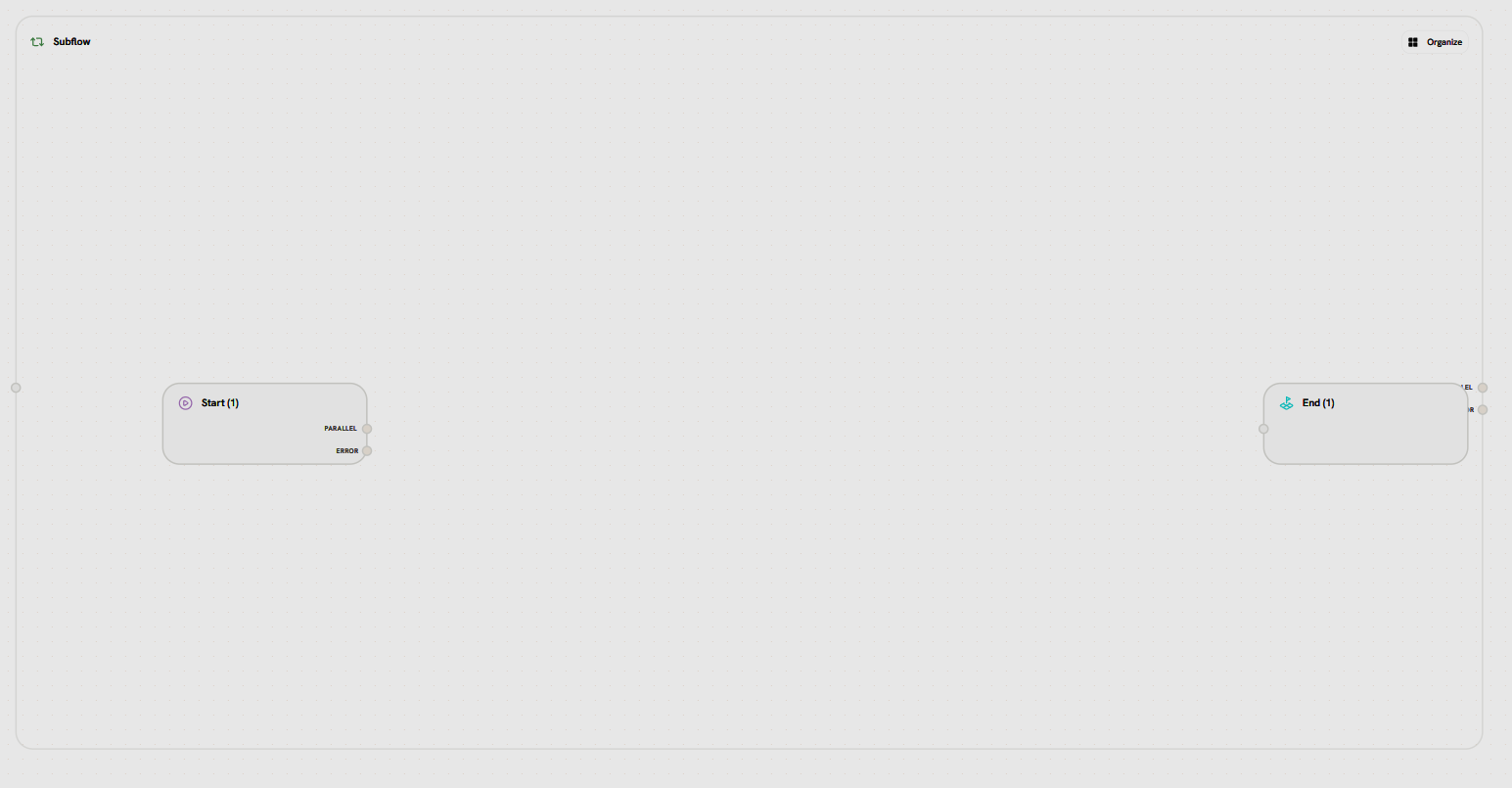
- Left: Start node (entry point to subflow)
- Right: End node (exit point from subflow)
- Canvas: Isolated workflow area for building reusable logic
- External Handles
- Internal Nodes
Parent Workflow ConnectionWhen viewed from the parent workflow, subflow nodes have standard handles:
- Input Handle (Left): Receives data from parent workflow
- Passes data to subflow’s Start node
- Triggers subflow execution
- Output Handles (Right):
- PARALLEL: Main output after subflow completes
- Returns data from subflow’s End node
- Continues parent workflow
- ERROR: Error handling path
- Activated on subflow execution errors
- Passes error details to parent
- PARALLEL: Main output after subflow completes
- Encapsulation: Isolated execution context
- Reusability: Use same subflow in multiple places
- Iteration: Can loop within subflow (agent patterns)
- Parameters: Pass data in/out via start/end nodes
- Resizing: Adjust canvas size to fit nested workflow
End Node
Purpose: Marks the end of a single iteration (in subflows) or workflow completion (in main workflows)
- Input Handle
- Output Handle
Left Side - Iteration/Workflow EndReceives data marking the end of execution flow.Accepts:
- Final output data from workflow/iteration
- Results to return to parent workflow (in subflows)
- Data to pass to next iteration (in loops)
- Multiple end nodes supported (different exit points)
- In main workflows: Marks workflow completion and returns output
- In subflows: Marks end of one iteration, loop may continue
- Output data passed to next iteration or parent workflow
End Node vs Stop Node in Subflows
- End Node: Completes the current iteration. If more iterations remain, execution loops back to Start Node.
- Stop Node: Immediately terminates the entire subflow, regardless of remaining iterations.
Stop Node
Purpose: Force-terminate subflow execution immediately Stop nodes set aForceFinish flag that exits the subflow loop, regardless of max_iterations.
- Input Handle
Left Side - Force Termination TriggerReceives signal to immediately terminate subflow execution.Accepts:
- Final output data before termination
- Completion signal from tools (e.g., “send_final_response”)
- Error conditions requiring immediate exit
- Immediate Termination: Stops all remaining iterations in the subflow
- Return to Parent: Parent workflow continues from the node after the subflow
- Iteration Override: Bypasses max_iterations check
- Last Output Returned: Returns the output from the most recent completed iteration
- Agent completes task and calls “send_final_response” tool → Stop
- Error condition requires immediate exit
- Task completion detected (no need for more iterations)
- Resource limits reached
- In Subflows
- In Main Workflows
Stops the entire subflow iteration loopEven if max_iterations = 10, the Stop Node immediately terminates the subflowParent workflow resumes immediately from the node after the subflow

